introduction:
You know that feeling when you read about an exciting new technology Solar Energy that seems futuristic but is actually happening right now? Concentrated solar power plants are one of those technologies that feel like they’re straight out of a science fiction novel, but they’re rapidly becoming a reality Solar Energy. CSP plants use mirrors to concentrate the sun’s energy and convert it into electricity that can power homes and businesses. The massive mirrored arrays capture and redirect the sun’s rays onto a central tower where the concentrated heat is used to Solar Energy generate power.
What Is Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)?
Concentrated solar power or CSP plants use mirrors to concentrate the sun’s energy and convert it into electricity.
How do CSP plants work?
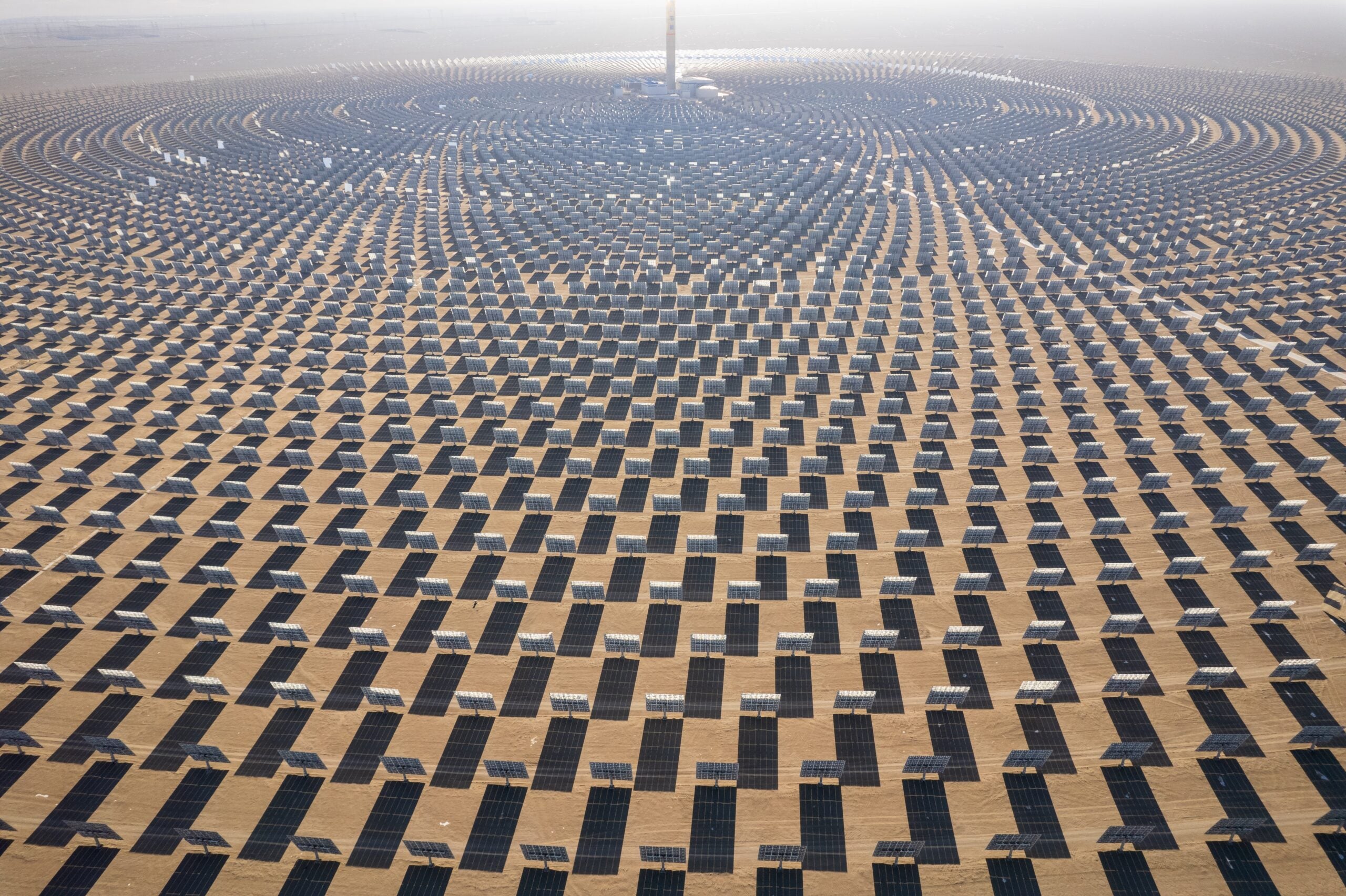
CSP plants use mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver that heats a liquid to high temperatures. The superheated liquid then makes steam which spins a turbine to generate power. There are three main types of CSP plants:
- Parabolic trough plants use curved mirrors to focus sunlight onto tubes of oil or molten salt. The heated fluid is then used to make steam.
- Power tower plants use arrays of mirrors called heliostats to concentrate sunlight onto a central receiver tower. The tower contains molten salt that is heated to over 1000°F and used to generate power.
- Dish/engine systems use dish-shaped mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver that powers a Stirling heat engine. The engine then drives an electric generator.
CSP plants allow for energy storage by heating molten salt and other fluids which can generate power even after the sun has set. CSP is a crucial technology for providing renewable baseload power that is available 24 hours a day.
With huge solar energy potential in hot, dry regions, CSP plants are poised to transform energy systems around the world. The future is indeed bright for this innovative solar technology.
How CSP Plants Work to Harness the Sun’s Energy
CSP plants are revolutionary because they’re able to harness the sun’s energy in a way that allows it to be stored and used when needed, not just when the sun is shining. Here’s how these futuristic power plants work their magic:
CSP plants use mirrors to concentrate the sun’s light to very high temperatures which then heat a fluid like molten salt. This molten salt can get hot enough to melt lead! The super-heated salt is then used to boil water and create steam which drives a turbine to generate electricity.
- Molten salt can retain heat for a long time, so it acts as a “thermal battery” that allows CSP plants to continue generating electricity even when the sun goes down or is obscured by clouds. The stored heat can produce power for up to 10 hours after sunset.
- CSP plants require very intensive sunshine to operate, so they are best suited for desert areas in sunny regions. Some of the largest CSP plants in the world are located in the Mojave Desert of California and the Sahara Desert of Morocco.
- The more the sun shines, the more power a CSP plant can produce. New technologies like solar power towers and parabolic troughs are making CSP plants even more efficient at turning the sun’s rays into usable energy.
The future is looking bright for CSP plants. As solar technologies advance, prices drop, and energy storage improves, these solar power plants could provide a major source of renewable energy across the globe, even after dark. The sun’s energy is abundant and eternal, and now we have a way to harness it 24 hours a day.
The Benefits of CSP Over Traditional Solar Panels
CSP plants offer several benefits over traditional solar panels.
Lower Costs
The initial costs to build CSP plants have dropped significantly in recent years, making them more affordable. They also have lower operating and maintenance costs since they have fewer moving parts. CSP plants can operate for up to 40 years, far outlasting the average 25-year lifespan of solar panels.
Greater Efficiency
CSP plants are more efficient at converting the sun’s energy into electricity. They can achieve up to 25% efficiency compared to 15-20% for solar panels. CSP plants also have built-in thermal energy storage that allows them to continue generating power even when the sun isn’t shining. The excess thermal energy is stored in molten salts to be used later. This gives CSP plants the ability to provide electricity on demand and dispatch power when it’s needed most.
Environmentally Friendly
CSP plants generate zero direct emissions since they don’t burn any fossil fuels. They require minimal water to operate and the little amount they do use is recycled. The fluids used in the solar collectors and turbines are non-toxic. At the end of their operational life, CSP plants can be decommissioned and the land restored without issue.
Job Creation
The CSP industry is creating many new jobs in manufacturing, construction, and plant operation. This is helping local communities by providing economic opportunities and a sustainable source of livelihoods for future generations.
CSP represents the future of solar energy. With continued innovation, CSP plants will get even cheaper and more efficient at harnessing the sun’s boundless power. The future is bright for this renewable and eco-friendly source of electricity!

CSP Plants Around the World – Where Are They Located?
CSP plants need intense sunlight to operate, so they are typically located in hot, arid desert climates close to the equator. The top regions for CSP plants are:
North Africa and the Middle East
Countries like Morocco, Egypt, and the United Arab Emirates have taken the lead in CSP development. The UAE’s Shams 1 plant and Morocco’s Noor 1 plant are among the largest CSP facilities in the world. This region receives abundant sunlight year-round, making it an ideal location for CSP technology.
South Africa
South Africa has also invested heavily in CSP, with several large plants located in the Northern Cape province. These plants provide renewable energy and economic opportunities to the region. Two of the biggest plants are the KaXu Solar One facility and the Xina Solar One plant.
Southwestern United States
The deserts of California, Nevada, Arizona, and New Mexico receive plenty of sunshine, especially in the summer. Large CSP operations like the Ivanpah Solar Power Facility, Solana Generating Station, and Mojave Solar Project are located in this region. The desert conditions are optimal for CSP, though some areas may experience reduced sunlight in the winter.
Chile and Peru
The Atacama Desert of northern Chile is one of the sunniest places on earth, with solar power potential off the charts. Chile’s Cerro Dominador plant is the first CSP facility in South America. Peru also has plans to develop CSP in the future to provide renewable energy for its growing population.
Australia
Australia’s hot interior deserts are poised to become a hub for CSP, especially in Queensland and South Australia. The country aims to obtain 23% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2020, so CSP will likely play an increasing role. Several demonstration plants have been built, with more commercial-scale projects in development.
With abundant solar resources and a need for clean energy, these regions are leading the way in CSP technology and helping to make the future brighter. By harnessing the power of the sun, CSP is revolutionizing how we generate electricity in an eco-friendly manner.
The Future of CSP – How It Can Revolutionize Renewable Energy
The future of CSP technology is incredibly bright. As the world transitions to renewable energy, CSP can play a pivotal role in revolutionizing how we generate and store solar power.
Greater Efficiency and Lower Costs
CSP technology is becoming more efficient and cost-effective. New innovations like molten salt towers and parabolic troughs are improving how CSP plants collect and store the sun’s energy. At the same time, manufacturing CSP components on a larger scale is driving down costs. The more CSP expands, the more affordable it will become.
Thermal Energy Storage
One of the biggest benefits of CSP is its ability to store the sun’s energy for use when the sun isn’t shining. CSP plants use thermal energy storage systems, like molten salt, to capture and retain the heat from the sun. The stored heat can then generate electricity for hours after sunset. This solves the intermittency problem of solar photovoltaic panels and allows CSP to provide baseload power.
Hybridization with Fossil Fuels
CSP can also be hybridized with natural gas or coal plants. The solar energy collected during the day could heat up the molten salt, which is then used at night to generate steam and produce electricity. The fossil fuels would only be used when the stored solar energy is depleted. This hybrid approach reduces emissions while ensuring a steady power supply.
Job Growth in Rural Areas
The growth of CSP provides economic opportunities, especially in hot, arid regions ideal for this technology. Constructing and operating CSP plants requires specialized labor and creates many new jobs in fields like manufacturing, engineering, and project development. These rural communities can benefit greatly from the job growth and tax revenues associated with CSP projects.
The future of CSP is bright. With greater efficiency, lower costs, energy storage, hybridization, and job growth, CSP can revolutionize how we generate and use solar energy. The more we adopt and advance this technology, the closer we move toward a renewable energy future.
Conclusion
So there you have it, concentrated solar power plants are changing the game for solar energy and our renewable future. While photovoltaic panels will likely still dominate solar for homes and businesses, CSP offers huge promise for utility-scale solar that provides power day and night. The technology is really taking off and costs are coming down fast. Within a decade, CSP could be cost-competitive with fossil fuels and provide a big chunk of power in sun-drenched parts of the world.
The prospects for CSP are incredibly exciting. Molten salt towers, parabolic troughs and solar dishes are futuristic technologies that are coming of age and ready to shine (pun intended!). While energy storage has long been the holy grail for renewables, CSP delivers and then some. So keep your eye on those funky mirrored contraptions out in the desert – they represent the future of solar and a bright future for our planet. The future is solar, the future is CSP!